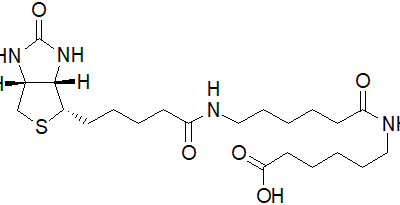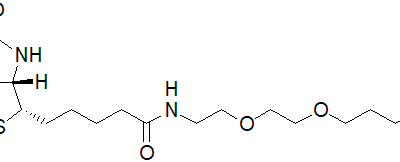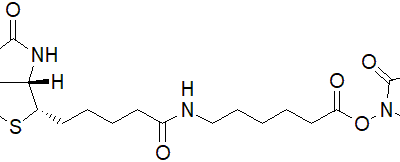Additional information
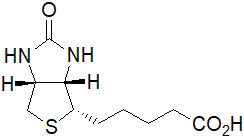
| Description | Biotin serves as a crucial coenzyme for specific carboxylases and is integral in modifying histones to regulate gene transcription [1,2,3]. Biotin-dependent carboxylases contribute to fatty acid and amino acid synthesis, as well as gluconeogenesis [1]. Beyond its metabolic roles, biotin finds applications in biotechnology, including DNA hybridization, flow cytometry, affinity purification, and the identification of protein-protein interactions and post-translational modifications [4]. |
|---|---|
| Reference | [1] Tong, L. Structure and function of biotin-dependent carboxylases. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 70(5), 863-891 (2013). |